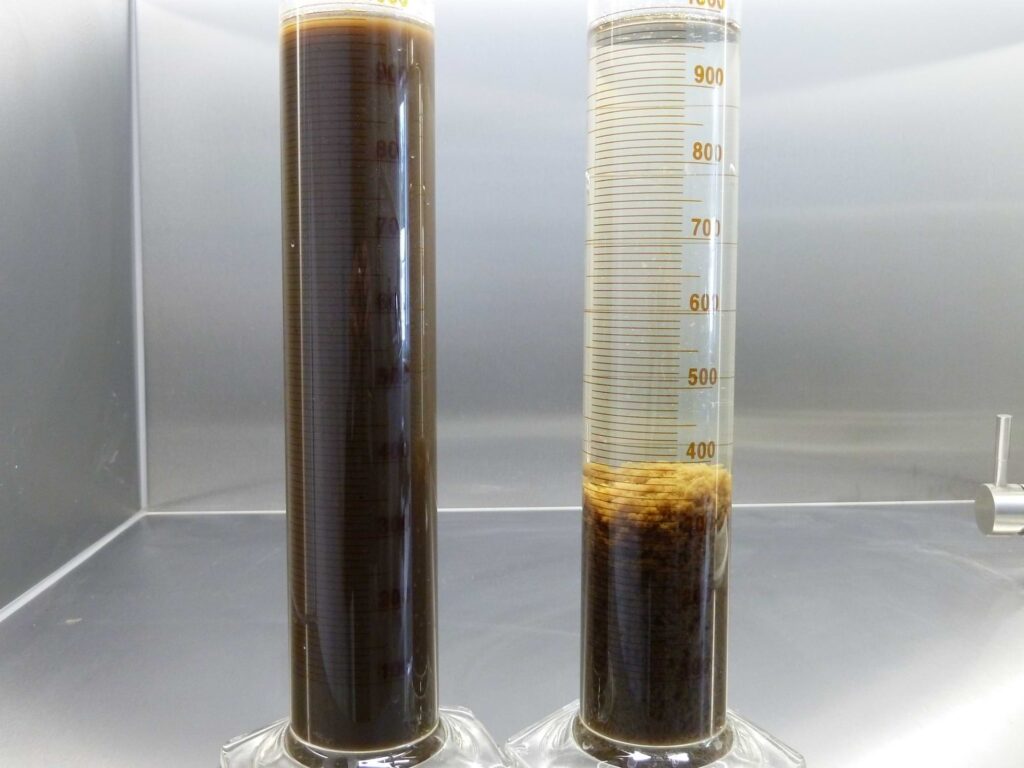
Improving sedimentation in wastewater treatment plants with a capacity above 200 000 RLM
Rapid improvement in sedimentation with extremely low doses
In recent years, there has been a change in the characteristics of domestic wastewater, including increased inflows of wastewater rich in fatty substances with the presence of lyophilic colloids (e.g., the development of home-based gastronomic points) and surfactants, especially non-ionic ones, which are more difficult to biodegrade in treatment processes. Additionally, the most popular and aggressive SPC compounds such as SLES, SDS, or LAS have become more prevalent. A significant increase in the quantity of detergents in wastewater was observed during the COVID-19 pandemic, when the use of disinfectants increased. Very often, the active ingredients in these products are quaternary ammonium salts or amphoteric amine oxides, which can reduce biological activity.
Wastewater treatment plants serving large urban areas may have a higher inflow of pollutant loads, including from various industrial sectors. Periodic issues with sludge sedimentation can occur for several reasons, such as overloading with pollutant loads, increased temporary inflow of sewage or rainwater, limitations in plant capacity, or ongoing renovation work.
To address these challenges and the market demand for a fast-acting, intervention tool to improve sedimentation, the DuoBent F500 preparation was developed. Previously, DuoBent preparations, in the case of high-capacity treatment plants, might have been associated with the need to dose significant quantities of the product, which required substantial operator involvement. Efforts were made to minimize the required dosage to achieve the desired effect.
The issue of increased periodic inflows of rainwater affects many wastewater treatment plants in Poland, whether due to their geographical location or general limitations in technological capacity. As demonstrated by the experiences from applications in treatment plants, DuoBent F500 can be used as an effective tool to prevent sludge flotation and, consequently, the uncontrolled escape of biomass in secondary settlers.
Additionally, DuoBent F500 can also be an effective tool for facilities receiving wastewater in tourist areas, which in a relatively short time or periodically throughout the year, receive significant pollutant loads. Often, biological systems designed for a specific capacity are not adapted to accommodate increased inflows, even if they occur temporarily.
By using DuoBent F500 at a wastewater treatment plant, you gain:
the possibility of quickly and interventionally improving sedimentation, even at wastewater treatment plants above 200,000 RLM,
a solution for wastewater treatment plants with a constant inflow of wastewater rich in fatty substances and surfactants, such as tourist destinations, hotels, extensive gastronomy, etc.,
improvement of sedimentation at extremely low doses – starting from 0.030 kg/m3 of the oxygenation tank volume,
a quick tool to use in the event of emergencies, biomass escapes, flow restrictions, process line shutdowns, upgrades, or increased rainfall runoff.
Feel free to familiarize yourself with the full content of the articles:
Learn more
Limiting the bacterial population of radiotrophic bacteria

Startup and Operation of the DuoFlow Mixer

Safe use of DuoBent








